
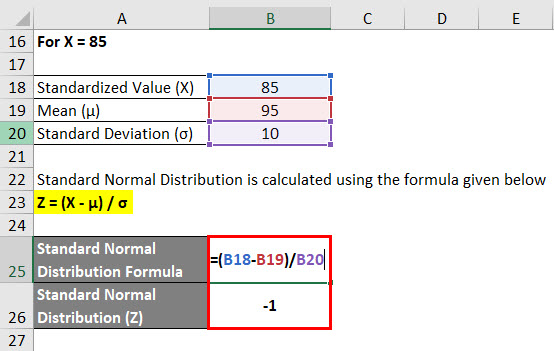
Then use the COUNTIF function (see Built-in Functions) to count how many times each score appears in the sample data. Alternatively use the Real Statistics QSORT and NoDupes functions as described in Supplemental Functions. The result appears in cell range C4:C8 above. The highlighted data can then optionally be sorted via Data > Sort & Filter|Sort. Thus, the probability that x takes a value t such that t 1 Data Tools|Remove Duplicates. Observation: If f is the frequency function of a discrete random x with distribution function F, then f( t) is the probability that x takes the value t and F( t) is the probability that x takes a value less than or equal to t. Proof: These are characteristics of the probability function P( E) per Property 1 of Basic Probability Concepts. Property 1: For any discrete random variable defined over the range S with frequency function f and distribution function F The corresponding ( cumulative) distribution function F( x) is defined at value t by the probability that x assumes the value t.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/05-Solver-Solution-ba9ad47cd0e14ce29c16ab2037cbe46e.jpg)
random variables that take a discrete set of values. Such random variables generally take a finite set of values (heads or tails, people who live in London, scores on an IQ test), but they can also include random variables that take a countable set of values (0, 1, 2, 3, …).ĭefinition 1: The ( probability) frequency function, also called the probability density function (abbreviated pdf), of a discrete random variable x is defined so that for any value t in the domain of the random variable (i.e. We now define the concept of probability distributions for discrete random variables, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
